Amanda
Answer Tips
Create Math Images
Labels
- Alvina (6)
- am40sw09 (8)
- Amanda (4)
- Camilla (5)
- Carmel (3)
- Chelsea (6)
- Class Survey (1)
- Compound Interest (2)
- Copyright (1)
- Daniel (5)
- David-san (1)
- Design and Measurement (2)
- Developing Expert Voices (16)
- Digital Ethics (1)
- Don (6)
- Dr. Eviatar (4)
- Eugene (5)
- First Post (1)
- Glenn (5)
- Henson (4)
- Homework (6)
- Iris (5)
- Jason (6)
- K_Hannah (5)
- Kathrine (2)
- Kayla (5)
- Kyle (6)
- Lamael (4)
- MAC (4)
- Matrices (22)
- Model Problems (2)
- Mr. Kuropatwa (69)
- Niwatori-san (4)
- Periodic Functions (6)
- Personal Finance (16)
- Pi Day (1)
- Post (1)
- Probability (33)
- Reflection (17)
- Scribe Post (57)
- Sequences (7)
- Sine Function (1)
- Slides (67)
- Sribe Post (1)
- Statistics (35)
- Statistics Reflection (1)
- Time Line (13)
- Vector (1)
- Vectors (15)
Blog Archive
-
▼
2009
(166)
-
▼
May
(51)
- so in class today we went over some of last nights...
- Today's Slides: May 28
- May 26th's and Today's Notes
- Today's Slides: May 27
- Today's Slides: May 26
- Transformation of the Sine function
- Today's Slides: May 25
- My Project Thing
- Today's Slides: May 22
- Today's Slides: May 21
- Developing Expert Voices
- Developing Expert Voices
- STUDY.STUDY.STUDY.Hey guys we have a test tomorrow...
- Today's Slides: May 19
- Developing MY Voice.
- Personal Finance... YEA!
- Developing Expert Voices
- So two questions I want to model over are vectors ...
- Thursday's Notes, DEV Project Tip
- Developing Expert Voices
- Developing Expert Voices
- Developing Expert Voices
- Developing Expert voices
- Developing Expert Voices
- Developing expert voices
- Dev. Project
- Developing Expert Voices: Respect Copyright & Reso...
- Today's Slides: May 14
- IT'S a LATE scribe POST
- May 12th on the 13th
- Today's Slides: May 13
- Today's Slides: May 12
- Leasing
- Today's Slides: May 11
- scribe post Friday May 8
- reflection #2 (vectors)
- Today's Slides: May 8
- Credit Card Interest Rates
- Today's Slides: May 7
- Compound Interest
- Today's Slides: May 6
- Reflection on Vectors
- Okay so today was our pre-test.We got into groups ...
- Reflection
- reflection
- Reflection
- Today's Slides: May 4
- REFLECTION!
- Reflection
- Vectors
- Today's Slides: May 1
-
▼
May
(51)
Thursday, May 28, 2009
Amanda
Posted by
don
at
10:25 PM
0
comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Don, Periodic Functions, Scribe Post
Today's Slides: May 28
Here they are ...
Posted by
Darren Kuropatwa
at
11:16 AM
0
comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Mr. Kuropatwa, Sequences, Slides
May 26th's and Today's Notes
As of the notes of Periodic Functions on May 26, we have learned and relearned of clarifying the amplitude, the period, and the phase shift.
To identify the amplitude, simply clarify the difference between the sinusodial axis and the maximum or mininum.
A period is determined through of the fraction 2(pi)/b. The parameter itself can be identified by switching 'b' with the period shown.

Parameter C is the phase shift. The phase shift moves the graph either left or right on the sinusodial axis, it is normally subtracted from x. The phase shift is identified as either a whole number or pi/c if the starting point value is less than a whole number.
We were also taught of the cosine function. But it bears a very close resemblence to the Sine function, so we'll only be learning of the Sine function this year. The difference from the Sine function is that it's starting point is pi/2 units apart.
For today's notes, we learn of Sequences, a list of numbers that follow a certain pattern. We learn of two types of Sequences, Recursive and Implicit. A recursive sequence, is a list of numbers generated by continuously adding the difference to the first term. Such an equation would be y= 3 ( n - 1 ) + 4, the 3 would be identified as the difference. Take note that n would be rank. An implicit sequence is basically a list of numbers generated by a linear equation. More or less y = 3 n + 1. The difference in an linear equation would be the slope.
With that said, this scribe will now bid you adieu. As he is sleep deprived, the next scribe will be Don. Please, the person that is to take care of the scribe list, please update it regularly. This is also for anyone next year as well. If, the scribe list is used again.
Posted by
Anonymous
at
3:03 AM
0
comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Glenn, Periodic Functions, Scribe Post, Sequences
Wednesday, May 27, 2009
Today's Slides: May 27
Here they are ...
Posted by
Darren Kuropatwa
at
2:56 PM
0
comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Mr. Kuropatwa, Sequences, Slides
Tuesday, May 26, 2009
Today's Slides: May 26
Here they are ...
Posted by
Darren Kuropatwa
at
10:40 PM
0
comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Mr. Kuropatwa, Periodic Functions, Slides
Monday, May 25, 2009
Transformation of the Sine function
Today in class, we learned what each parameter in the sine function does.
This is what a sine function formula looks like:
but.. what does the formula mean?
Let's start with Parameter D:
- a (+) value shifts the graph upwards by
x number of units
- a (-) value shifts the graph downwards
so..if D = 2, the graph shifts up 2 units
if D = -2, it shifts down 2 units

Parameter A:

Parameter A controls the amplitude of
the graph
* The amplitude gets higher when the value of
gets bigger. A negative value will flip the wave
upside down, but the height of the wave does
not change.
Example:

-the black wave is what a basic
function looks like
- the blue wave represents the function with
a negative A value (A=-2)
-the red wave represents the function with a
positive A value (A= 2)
Parameter B:

Parameter controls the width of the
graph. It also multiplies the copy of
the wave.
normal sine function : period = 2π
so...B= 2 is the same as 2π/2 or π
* the value of B becomes divides the
normal sine function.
Example :

- black wave : sin(X)
- red wave : sin (2X)
Parameter C:

Parameter C shifts the graph
left and right
- a (+) value shifts the graph
to the left by x number of
units.
- a (-) value shifts the graph
to the right.
Example:

- black wave - represents the basic
sine function
- red wave - represents a positive C
value ( C=2)
- blue wave - represents a negative C
value (C= -2)
That's it for today's blog. I hope it helped you guys understand the today's topic.
The next blogger will be... Roe.
Posted by
Lamael
at
11:52 PM
1 comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Lamael, Scribe Post, Sine Function
Today's Slides: May 25
Here they are ...
Posted by
Darren Kuropatwa
at
2:36 PM
0
comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Mr. Kuropatwa, Periodic Functions, Slides
Sunday, May 24, 2009
My Project Thing
for one of the questions (since my computer wont let me view past posts/videos, i am just remembering back to a question i remembered from matrices about trips between cities.
I will figure out the details once i get with my partner.
My second question is from the unit of probability.
On the board game you can move pieces diagonally forward.
a) determine the number of different pathways from the game piece to each of the squares on the other side of the board.
b)assume the player is equally likely to go left or right. what is the probability it will land on each destination.
My timeline is the same is chelsias
Posted by
K_Hannah
at
10:09 PM
1 comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Developing Expert Voices, K_Hannah, Time Line
Friday, May 22, 2009
Today's Slides: May 22
Here they are ...
Posted by
Darren Kuropatwa
at
4:07 PM
0
comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Mr. Kuropatwa, Periodic Functions, Slides
Thursday, May 21, 2009
Today's Slides: May 21
Here they are ...
Posted by
Darren Kuropatwa
at
3:47 PM
0
comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Mr. Kuropatwa, Periodic Functions, Slides
Developing Expert Voices
Questions:
a.) Statistic Problem
For boys, the average number of absences in the first grade is 15 with a standard deviation of 7; for girls, the average number of absences is 10 with a standard deviation of 6.
In a nationwide survey, suppose 100 boys and 50 girls are sampled. What is the probability that the male sample will have at most three more days of absences than the female sample?
b.)Vectors
Draw scale diagrams of the following vectors using pencil, ruler, protractor, and paper. Label the diagram. Be sure to indicate the scale you used.
(1.) Tiffany walks 13 blocks in a direction East 13 degrees South.
(2.) A boat is headed 300 degrees at 45 km/h.
Time line
May 22 - rough draft questions
May 25 - consult with partner(s)
May 29 - rough copy
June 03 - completion of the project
June 04 to 05 - hand in the project
Posted by
Anonymous
at
8:47 AM
0
comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Developing Expert Voices, Jason, Time Line
Wednesday, May 20, 2009
Developing Expert Voices
Question 1 : Personal Finance
Debt. Equity Ratio = Total Liabilities - Mortgage / Networth
Lebron is married with two childen. He wants to borrow money to make a major purchase.
His financial advisor prepares a net worth statement for his family with the following.
Lebron and his family live in an $80,000 home on which there is an outstanding mortgage of $52,000.00. He owns a car valued at $20,000.00 and owes 12,000.00 on a 2-year loan he took to buy the car. He has $5000 and a short term personal loan for $2500.00. The family has $1500.00 in a chequing account and another $3000.00 in a savings account. He owns a boat worth $5000.00
Question 2 :
Timeline
May 24: Rough Copy for Questions & Solve Questions
May 25: Create visuals for project
May 26 - 31: Put together all visuals on computer
June 1 - 6: Complete Project
June 7: Hand in Project
Posted by
MAC
at
12:31 AM
1 comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Developing Expert Voices, MAC, Model Problems, Time Line
Tuesday, May 19, 2009
Today we learned that that net worth = assets-liabilities.
Assets is money you have or things of value that you own. There are three kinds of assets:
Liquid Assets: Money you can access easily (cash amounts)
Semi-Liquid Assets: Longer term investments (stocks, mutual funds, or some real estate)
Non-Liquid Assets: Material goods (cars, houses) you have to sell it to make money.
Liabilities is amounts of money that you owe. There are two kinds:
Short Term Debts: Must be paid in the next twelve months.
Long Term Debt: Payments that will take more than a year (mortage).
We also learned today that the Debt/Equity Ratio = (Total Liabilities - Mortage) / Net Worth
You want the outcome of the Debt/Equity Ratio to never be bigger than .5 or 50%. If it is even half a percent higher you will have a hard time finding a bank if you can that will give you a loan. But not is all lost, if it is larger than 50% you may try to get a lower loan, find the money in some bond or somewhere else, take a smaller loan then get another after, or even pay off another debtin order to get that percent 50 or lower.
There a few really good examples of this in the slides Mr.K has put up, so if you feel you need more feel free to also look there.
Wish everyone luck on tomorrows test :) and the next scribe is...Lamael
Posted by
iamamanda
at
8:12 PM
0
comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Amanda, Personal Finance, Scribe Post
Today's Slides: May 19
Here they are ...
Posted by
Darren Kuropatwa
at
12:34 PM
0
comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Mr. Kuropatwa, Personal Finance, Slides
Developing MY Voice.
That's problem one. Problem two will be based on a suggestion Mr. K made about the probability of being drafted. I don't think we ever actually did a question of it though...
Timeline:
By May 25th I will have completed my questions. By June 3rd, I will have filmed portions to be embedded in a prezi presentation. By June 6th, I will have completed my prezi and published it to the blog.
Posted by
Daniel
at
10:48 AM
0
comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Daniel, Developing Expert Voices, Time Line
Personal Finance... YEA!
Alright, let's get this started with a concept I was stumbling with for a bit. I could not, for the life of me, understand why the formula for the feasible financial capital percentage one should consider when purchasing a home. For your information, the absolute maximum feasible percentage of one's income that should go towards their home is 32%. Here's a couple things to remember.
It's called the GDSR, and it's composed of a number of things. You've got your Monthly Mortgage Payment, your Monthly Property Tax Payment, your Monthly Heating Bill, and half of your Condo/Strata Fees. Now you lump that all together into one great big chunk and you divide it by your Monthly Income. The number that is generated will be a decimal, in theory. Technically, if you were using this formula on a house WAY out of your range, you'd get a whole number. Or, over 100% of your monthly income would be going to your house.
That's right! The decimal you receive is a percentage! And that is the percentage of your income that is going to your house. You want that to be under 32. The formula looks like this:

Perhaps you are thinking, "That's all well and good, but what if I'm missing a variable, smart-guy!? Maybe I don't know my monthly mortgage payment, JERK!" Well fear not my fine, feathered friend. If you find 32% of your income, and subtract from it what you DO know, your answer will be what remains of your 32% income, or, what you have at your disposal for whatever variables you are missing. For example:
If I have $1000 a month for housing, my feasible income percentage will be $320. Let's say it's a house, BOO-YEA, no condo/strata fees. Heating is %40 a month, property taxes are $60. BEAR WITH ME.... $40+$60 is $100, Therefor... $320 - $100 = $220. I have $220 to spend on housing per month.
The other thing we covered today was the pros and cons of home ownership. For more information contact your local "Personal Finance" tagged slide... uh..(s)... Slides.
Posted by
Daniel
at
10:19 AM
0
comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Daniel, Personal Finance, Scribe Post
Developing Expert Voices
Question #1 Personal Finance Unit
Shaiana wishes to invest $2000.00 given by her grandfather. She has an option guaranteed earning investment certificated of 8.5%, compounded quarterly, or a savings bond of 9%, compounded semi annually.
Which investment should she choose?
If each investment is termed 5 years, what will the difference of their values be at the end of the term?
Question #2 Matrices Unit
On the soap opera, the young and the mathematical Ann is in love with Buck and Dash. Dash is in love with Ann, Charlotte and Elvira. Charlotte who just broke up with her fiancé after learning that he was dating the University of Winnipeg women's basketball team, has fallen in love with Frank, not realizing that he is actually her step brother who has returned to Winnipeg with amnesia and major plastic surgery after the tragic explosion of a graphing calculator at a secret CSIS cryptography lab. Frank is in love with Elvira. Buck is in love only with himself. Write a connection matrix detailing the relationships among the six named characters. Include labels and other explanations to make your work clear.
Time Line:
May 23: Rough Copy for Questions & Solve Questions
May 24: Create visuals for project
May 25 - 31: Put together all visuals on computer
June 1 - 6: Complete Project
June 7: Hand in Project
Posted by
iris
at
10:16 AM
0
comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Developing Expert Voices, Iris, Time Line
The next question I choose is this one
 I chose this one because I failed my statistics test and this was one of the hardest things to do on the statistics unit in general. Normal curves were just a bit confusing. Okay so these are the questions im going to model my expert voices project on albeit a little more difficult and a little bit more different.
I chose this one because I failed my statistics test and this was one of the hardest things to do on the statistics unit in general. Normal curves were just a bit confusing. Okay so these are the questions im going to model my expert voices project on albeit a little more difficult and a little bit more different.
Posted by
henson
at
10:11 AM
0
comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Developing Expert Voices, Henson, Time Line
Thursday's Notes, DEV Project Tip
For the notes on thursday, May 14, we were reminded of how to calculate our GDSR. Or otherwise, our Gross Debt Service Ratio. Our GDSR will not allow more than 32% of our income to be spent or else you want to spend your time bored and hungry. Your Gross Debt Service is calculated by summing the monthy mortgage payment, the monthly property tax, monthly heating costs, and half of your condo fees if you're living in a condo. The sum of this will be divided by your Gross Monthly Income (this includes people who are living with you, unless they are minors).
The formula will be shown here.
In order to find out how much you can afford each month (the monthly mortgage), multiply your GMI by 32% and subtract the sum of the monthly payments with the product of the GMI and GDSR.
With this, we've found the monthly mortgage for this
Once finding the monthly mortgage, we can find the Maximum Mortgage Payment of an individual or a group of individuals. To calculate this we input this into the TvM Solver, the payment periods are set to monthly while the interest compounding periods are set to semi-annually. Once we find the principle value or PV, we simply add it to the down-payment to get our MMP.
Example:
There are additional costs to buying a house though.
1. Appraisal fees
2. Inspection costs
3. Property Survey
4 Insurance costs for high ratio mortgages
5. Home insurance
6. Land transfer tax
7. Interest adjustments
8. Prepaid property taxes and utilies
9. Legal fees
10. Sales tax
11. Moving expenses
12. Services cgarges
13. Immediate repairs
14. Appliances
15. Decorating cost
To find the additional costs, clarify all of the costs and sum them.
A reminder tip for the DEV project.
If you're using slides, do not turn them into power point projects. Always use short, attractive bursts of information with a large amount of images to support said information. Sometimes even an image itself is good enough to bring out what you want to say. Don't be afraid to use a lot of slides.
...the next scribe is Daniel as I didn't see his post. If he isn't there Amanda is next. If she isn't there, Camilla's next.
Posted by
Anonymous
at
1:12 AM
1 comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Glenn, Personal Finance, Scribe Post
Monday, May 18, 2009
Developing Expert Voices
#1 Matricies
Given these matricies: 1. For each operation listed below, state if it is possible to perform the operation or not.
1. For each operation listed below, state if it is possible to perform the operation or not.
(a) A + C (b) B + C
(c) 2.2A (d) 2A - 3C
(e) AB (f) BC
2. Perform each of the following operations.
(a) C + 2B
(b) 3A
(c) CA
#2 Personal Finance
Camilla wants to drive a small economy car priced at $19 800 before taxes. PST is 7% and GST is 5%. She has $3 500 to use as a down payment for buying. If she buys the car, she will get a 4 year loan at 8.5% to pay for it. What is the total cost of buying the car?
Time Line:
May 23/24 - I will have my first problem done.
May 25-29 - I will work on my next two problems.
May 30/31 - I will have all 4 problems finished and looked over.
June 1 - I will start my reflection.
June 6 - I'll have my presentation published.
Posted by
Camilla
at
11:13 PM
1 comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Camilla, Developing Expert Voices, Model Problems, Time Line
Developing Expert Voices
Developing Expert Voices
Question #1Probability test Part IV problem solving
1) A multiple choice test has five questions with four choices for each question. a student guesses at all the answers without reading any questions.
a)What is the probability that she will get all the answers correct?(2 marks)
b)what is the probability she will get exactly three answers correct?(2 marks)
c)what is the probability she will get at least one answer correct? (2marks)
Question #2
Vectors Pre-test question 5
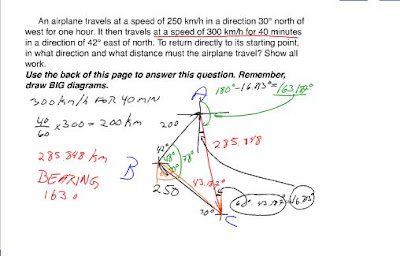
5) an airplane travels at a speed of 250 km/h in a direction 30 degrees north of west for one hour. it then travels at a speed of 300 km/h for 40 min ina direction of 42 degrees east of north. To return directly to its starting point, in what direction and what distance must the airplane travel? show wall work use the back of pag to answer this question remeber draw BIG DIAGRAM
Time Line
May 22
Consult with group (alvina and katie) about what units are project are on and if we ahve a theme to follow. all aroudn get organized.
May 25
meet up in library assign tow questions to a person and help if needed. decide how the project will be put across to the class. Eg: video, slide etc...
May 27
meet up at library or katies house to help eachother wityh any problems...
June 1
put completes questions of the project together.. of whatever we have.
June 3
Start publishing to computer
June 5
complete all finishing touches and hand it in!
Posted by
Chelsea
at
11:00 PM
1 comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: am40sw09, Chelsea, Developing Expert Voices, Time Line
Developing Expert Voices
Question #1: (March 27; Statistics)
The table shows the lengths in millimetres of 52 arrowheads.
(Didn't type out the numbers, but will create a similar question to this one.)
(a) Calculate the mean length and the standard deviation.
(b) Determine the lengths of arrowheads one standard deviation below and one standard deviation above the mean.
(c) How many arrowheads are within one standard deviation of the mean?
(d) What percent of the arrowheads are within one standard deviation of the mean length?
Question #2: (March 17; Probability)
The probability that Gallant Fox will win the first race is 2/5 and that Nashau will win the second race is 1/3.
1. What is the probability that both horses will win their respective races?
2. Wha tis the probability that both horses will lose their respective races?
3. What is the probability that at least one horse will win a race?
Time line
May 20 - Consult with the group and decide which units were going to do our projects on.
May 22 - Make sure that everyone has slowly progressed on their projects and help each other out on what their missing.
May 25 - Another group meeting, making sure everyone has got something done.
May 30 - Start putting bits an pieces of our project together.
June 3 - Complete Project
June 4 -6 - Put the finishing touches on the project
June 7 - Hand in completed assignment
Posted by
Kyle
at
10:28 PM
1 comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Developing Expert Voices, Kyle, Time Line
Developing Expert voices
March 16, 2009
Rupert has either milk or cocoa to drink for breakfast with either oatmeal or pancakes. if he drinks milk, then the probability that he is having pancakes with the milk is 2/3. the probability that he drinks cocoa is 1/5. the probability that he drinks cocoa is 1/5. if he drinks cocoa, then probability of him having pancakes is 6/7.
a) show the sample space of probabilities using a tree diagram or an other method of your choice.
b) find the probability that Rupert will have oatmeal with cocoa tomorrow morning.
May 14, 2009
Lucy Brown wants to buy a condo, but does not know how much money she should spend based on her income. She earns $44 000 per year, and has saved $9000 for a down payment. the propery taxes for the condo she likes are $1500 per year, and the heatig costs average $90 per month. the condo/strata fees are $18 per month, the bank will give her a 250 year mortgage at an interest rate of 7.5%. what is the maximum price she can afford for a condo, based on spending no more than 32% of her gross income on household and accommodation expenses?
Timeline
May 20 - Consult with the group and decide which units were going to do our projects on.
May 22 - Make sure that everyone has slowly progessed on their projects and help eachother out on what their missing.
May 25 - Another group meeting, making sure everyone has got something done.
May 30 - Start putting bits an peices of our project together.
June 3 - Complete Project
June 4 -6 - Put the finishing touches on the project
June 7 - Hand in completed assignment
Posted by
don
at
9:37 PM
1 comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Developing Expert Voices, Don, Time Line
Developing Expert Voices
Questions :
March 5 : Probability
(1) The cafeteria special for lunch offers a choice between two main courses (hamburgers or chicken burgers) and three different drinks. The "meal deal" allow you to pick one of each. How many different "meal deals" are they offering?
What if they offer to throw in a choice of fries, spicy fries of plain chips; how many "meal deals are they offering now?
May 12 : Personal Financing
(2) A group of rural students is planning to go to university. One of the members of the group suggests that they purchase an older home rather that rent an apartment. After a careful analysis of their finances, the group decides that their gross monthly income would be $3000.00. Monthly property taxes are estimated to be$125.00. Heating bills are estimated to be $150.00. The group can arrange a mortgage at a rate of 9%. The three members of the group are able to come up with a down payment of $8000.00 Determine he maximum affordable purchase price that can be considered if they take out a 25 year mortgage.
March 12 : Probability
(1) Suppose that, when you go home from school, you like to take as great a variety of routes as possible, and that you are equally likely to take any possible route. You will walk only east or south.
(a) How many ways can you go from the school to home?
(b) What is the probability that you will walk past the post office on your way home?
Time line
May 22 - complete all rough draft questions and ideas.
May 25 - consult with group / partner with the idea and questions
May 29 - rough copy Online.
June 3 - complete the project.
June 4 - 5 add little touch ups to project and hand in published project.
Posted by
alvina
at
7:26 PM
1 comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Alvina, Developing Expert Voices, Time Line
Sunday, May 17, 2009
Developing expert voices
Timeline
Today 05/17/09: Publish this post
05/21/09: Create Problems from above Models
05/22-29/09: Complete Problems, ask for help from Mr. K. if needed
05/30/09: start to publish assignment
05/30/09-06/07/09: Hand in published assignment
Posted by
Eugene
at
3:42 PM
0
comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Developing Expert Voices, Eugene, Time Line
Friday, May 15, 2009
Dev. Project
Questions:
March 12, 2009 Probability
Suppose that, when you go home from school you like to take as great a varitey of routes as possible, and that you are equally likely to take any possible route. You will walk only east or south.
How many ways can you go from the school to home?
What is the probability that you will walk past the post office on your way home?
May 4, 2009
A ship needs to travel in the direction of 40'. The ship has a speed of 20 knots in still water. A current of six knots at 340' is pushing the ship. Determine the direction the ship is headed and the magnitude of the ship's resultant velocity.
Time Line:
May 25th: Rough Copy for Questions
May 29th: Rough Copy for Online Portion of Project
June 5th: Complete Project
June 7th: Hand in Project
Posted by
Kayla
at
8:12 PM
0
comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Developing Expert Voices, Kayla, Time Line
Developing Expert Voices: Respect Copyright & Resources For You
We talked more about your upcoming Developing Expert Voices projects today. First some resources you can use to put together your online presenations:
The 50 Web 2.0 Ways to Tell a Story Wiki
Remember? The story about the dog Dominoe told in over 50 very cool ways. The video was good (here it is as a slidecast below) but I think everyone was really impressed with the Prezi version.
We also talked a little about presentation design:
As you collect various digital artifacts to string together your project keep in mind you must respect copyright; you can't use ("steal") other people's work without permission. Here are two videos that illustrate some of these ideas. Below them you'll find links to sites where you can find Creative Commons copyrighted music and pictures.
A Fair(y) Use Tale
Creative Commons: Wanna Work Together?
Find Creative Commons music at Jamendo.
Find Creative Commons licensed pictures using the flickr creative commons search tool.
Posted by
Darren Kuropatwa
at
12:29 PM
0
comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Copyright, Developing Expert Voices, Mr. Kuropatwa
Thursday, May 14, 2009
Today's Slides: May 14
Here they are ...
Posted by
Darren Kuropatwa
at
3:20 PM
0
comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Mr. Kuropatwa, Personal Finance, Slides
Wednesday, May 13, 2009
IT'S a LATE scribe POST
Hi, Today in class the first thing we did was hand in the answers to our homework.Then Mr. K. went over the answer after we handed it in. After that we talked about the advantages of leasing and buying a vehicle.
ADVANTAGES LEASING
- Lower initial Payments
- Get to drive most recent vehicles (new)
- Can not modify the Vehicle
ADVANTAGES BUYING
- You own the vehicle it is yours
- You have an unlimited amount if kilometers
- You can modify your vehicle
Shortly after we talked about buying and renting a house. Renting is basic it is monthly payments( + hydro, water etc. if not included in rent). But you will never own the house if you rent it.
Buying a house is quite different. You must have a minimum down payment of 5% of the value of the house.
EX: A house is valued at $100,000 your minimum down payment will be $5,000
how? value(100,000)*minimum down payment of 5%(.05)
=$5,000
Then you have to get a mortgage. A mortgage is like a loan from the bank that you have to obviously payback but with interest.
EX: The mortgage will cost you $106,400
how? balance($95,000)+ total interest($11,400)
=$106,400
The Mortgage balance is what is left over from the total value of the house after the down payment is made.
Also Mentioned In Class
The GDSR-Gross Debt Service Ratio is how to find out he maximum amount of your income you can afford on a house (32%).This can be expressed as a formula:
GDSR=Mo. Mort. pmt.+Mo. Prop. tax+Mo. heating cost+ 1/2 of condo or strata fees
Gross Monthly Family Income
Equity-The part of the house you own.
Next Scribe is:DANIEL
Posted by
Eugene
at
10:48 PM
0
comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Eugene, Personal Finance, Sribe Post
May 12th on the 13th
Well I made a post last night.... but it didn't seem to publish. I was having a hard time publishing it.. kept getting an error message and eventually it said it posted... but apparently not. Anyways... lets see how close I can get to the previous post that never made it up.
Well we continued to use the same program through APPS then into Finance.
We also talked about Depreciation value.
Depreciation is the amount of value a thing loses. The depreciation Rate is how much value it loses per time period. weather it be week... month or maybe year.
An example would be if a car lost 10% of its value every year... and lets just say the car was worth $10,000.00, after one year the car would be worth $90,000.00. Now this is the part you have to remember. when it comes to the price after the second year, you cant just take 20% off of the initial price ($100,000). you have to take 10% off of the value at the end of the 1st year (the $90,000.00).
There are two ways of doing this... you can either make a chart that looks like ..
Year initial value End of year
1 $10,000 $90,000
2 $ 90,000 $81,000
3 and so on...........
OR,,,
you can use the formula I(r)^n
I=initial amount
r= depreciation rate
n=number of years (or whatever the time period is at which the depreciation value is based upon)
WE ALSO:
we also looked deeper into leasing. We discussed how when u lease a car... you are only paying for the part of the car u are using because at the end of your lease... u have to give back the car. Now when you give it back, it is not worth as much as it was when you first got it.
Leasing a car is like asking for a bite of food. You still get to taste it.... but you don't get the whole thing. You enjoy your piece, then give the rest back.
As I was saying before, the depreciation is the value of the car that you have used up.. and the value that u give back to the dealer is called the residual value.
Since you use up the depreciated value, you have to pay sales tax on that part. You do not however have to pay taxes on the residual value.
Much like today, we went over some of the Pros and Cons to both leasing and Buying.
Leasing a vehicle is good for someone who can only afford small monthly payments, who doesn't want to worry about dealing with trading in or selling a vehicle when they no longer want it or who likes to change vehicles often.
Buying a vehicle on the other hand is good for someone who can afford to outright buy a car, who used a vehicle allot (travels long distances, across town commute etc.) or who likes to make customizations to their vehicle.
That is about all the things we went over....
I already chose the scribe for today but i will just put it up anyways for record sake ( Eugene )
I apologize again for not posting it last night... i really thought it was up.
Posted by
K_Hannah
at
9:06 PM
0
comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: K_Hannah, Personal Finance, Scribe Post
Today's Slides: May 13
Here they are ...
Posted by
Darren Kuropatwa
at
12:34 PM
0
comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Mr. Kuropatwa, Personal Finance, Slides
Tuesday, May 12, 2009
Today's Slides: May 12
Here they are ...
Posted by
Darren Kuropatwa
at
12:32 PM
0
comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Mr. Kuropatwa, Personal Finance, Slides
Monday, May 11, 2009
Leasing
Hey everyone! Today in math class, we learned about leasing. We started the day with the usual 'going over the homework' and then Mr. K put us right into the lesson on leasing.
From what I understand, leasing is when someone is giving another person either land, property, car, etc. to another person for a certain amount of time. Its like a rental agreement that can last for years. What also happens is that people who are leasing, have to make monthly payments for
•'depreciation'
•'sales tax' to that depreciation
• and 'interest on the unpaid value' of the item that is being used.
Depreciation means that there is a reduction of value in that item as time passes by. For example, the more you wear a brand new pair of jeans and as time goes by, the jeans start to fade out, decreasing the value of the jeans.
Sales tax is the tax that has to be paid for a section of that item that is being used. For example, a car that you decided to lease for three years, you only pay a portion for the car because you only use it for a certain amount of time and then you have to give the car back. During the time you have the car, you are paying taxes for the portion that you used.
Interest is when you pay at a particular rate for what you are leasing
When you are done leasing the item, You would either return it to the person that loaned you the item or you can buy the item. What this is called is 'Residual Value'. It's the amount (cost) of the being sold.
Mr. K also showed us a way to see how depreciation works with the calculator.
Ex. A car depreciates 20% per year. What is it worth in 5 years?
This is what it would look like on the calculator
What we did was you take 100% and subtract 20% from it, giving you 80%
Then we did 100*0.80 which equaled to 80.
What you would do next is you have to press on the multiplication button on your calculator and then it what would pop up is Ans* and then you punch in 0.80.
Press enter 4 more times to give you how much it would be worth in 5 years.
The car is worth 32.768 in five years.
The next scribe will be, K_Hannah (:
Posted by
alvina
at
9:03 PM
0
comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Alvina, Personal Finance, Scribe Post
Today's Slides: May 11
Here they are ...
Posted by
Darren Kuropatwa
at
12:38 PM
0
comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Mr. Kuropatwa, Personal Finance, Slides
Sunday, May 10, 2009
scribe post Friday May 8
Sorry for the late scribe post...
Scribe post May 8/09
Today we opened up the class by seeing a pink smart car with hello kitty on it, it was cute... in a "i would never do way" but cute.
We learned how to see how much of your savings and what interest you will have after a certain amount of months, years so on.
in the case that Mr K had given us the payments where made quarterly so for instance with the example he had given us..i had broke it down on the image below... The next question we worked on showed us how to not only to find the monthly payment but to also find out the complete interest you received and how much it would be to pay it off..
The next question we worked on showed us how to not only to find the monthly payment but to also find out the complete interest you received and how much it would be to pay it off..
a monthly payment of $8250 loan with a interest rate of 8.5% compounded monthly...If the loan is repaired in 2 years (24 months)
to determined the monthly payment we go to are tvm solver on our calculator under finance and fill it out like this... the pmt (payment) amount was -376.52 because you are taking it FROM your money to pay it off.
the pmt (payment) amount was -376.52 because you are taking it FROM your money to pay it off.
To determine the total cost of Repaying the loan would be 376.52* 24
---24-- because of the 24 month payment
= 9036.48
You take that amount and subtract the principle value, so the value you started with .
9036.48-8250= $786.48
Sorry again for the late scribe post if anything is wrong with this scribe please comment so i can fix it!
thank you see you Monday!
next scribe is...Alvina!
(if Alvina had done it already then .....Katie!)
Posted by
Chelsea
at
11:01 PM
0
comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: am40sw09, Chelsea, Personal Finance, Scribe Post
reflection #2 (vectors)
This is my reflection on vectors
This unit was one of the shortest ones i have ever done, i understood most of it other then the Parallelogram Method, and when all the questions were put into super complicated problems where words were switched around. That was the only time i was somewhat lost. Other then that i got everything i was so excited and proud, it was taught well and pretty easy understood.
:)
...sorry was late...
Posted by
Chelsea
at
10:56 PM
0
comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: am40sw09, Chelsea, Reflection, Vectors
Friday, May 8, 2009
Today's Slides: May 8
Here they are ...
Posted by
Darren Kuropatwa
at
3:20 PM
0
comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Mr. Kuropatwa, Personal Finance, Slides
Thursday, May 7, 2009
Credit Card Interest Rates
Hi guys..We've just discussed about our assignment and it was really interesting. We also discussed about Credit Cards and Interest Rates. There are 2 types of interest rate:
Nominal Interest Rate is the interest that the bank given.
For example: If the bank has 5% interest rate in semi-annually, the Nominal Interest Rate would be 10%. It will be 10% percent because semi-annually is half a year and annually get charged. Like:
05%(2) =10% (2) - represent a 1/2 year
and Effective Interest Rate is the rate that you actually charge on an annually basis and or paying interest on interest each compounding period.
Here are the Solution to get the Effective Interest Rate:
Effective Interest Rate = ( 1 + i / m ) ^m -1
Effective Interest Rate = ( 1 + 0.10 / 2 ) ^2 -1
Effective Interest Rate = ( 1 + 0.05 ) ^2 -1
Effective Interest Rate = ( 1.05 ) ^2 -1
Effective Interest Rate = 1.1025 -1
Effective Interest Rate = 0.1025
or = 10.25%
NOTE :
m - is the number of compounding period like:
Monthly (12), Quarterly (4), Semi-annually (2) and Weekly (52)
i - is the Nominal Interest Rate.
! This website might give you some great ideas about Interest Rates and solution to your questions:
http://freeonlinecalculator.net/calculators/financial/effective-interest-rate.php
In addition to, we also discussed about the "Rule of 72". The "Rule of 72" is a simplified way to determine how long an investment to take double, given a fixed annual rate of interest.
Formula of "Rule of 72" is:
Years = 72 / ( Interest Rate % )
Rate = 72 / Years
http://www.investopedia.com/ask/answers/04/040104.asp and or
If you have questions and complains to my post, i really appreciate to send me a comment.
Next Scribe is Chelsea.!!.
Posted by
Anonymous
at
9:45 PM
0
comments
![]()
![]()
Labels: Compound Interest, Jason, Scribe Post
Chatbox
Contributors
Links
Recent Comments
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 2.5 Canada License.